The following is an aerodynamic shape optimization case for the NACA0012 airfoil at low speed:
Case: Airfoil aerodynamic optimization Geometry: NACA0012 Objective function: Drag coefficient (CD) Lift coefficient (CL): 0.5 Design variables: 20 free-form deformation (FFD) points moving in the y direction, one angle of attack Constraints: Symmetry, volume, thickness, and lift constraints (total number: 34) Mach number: 0.02941 (10 m/s) Reynolds number: 0.6667 million Mesh cells: ~4,000 Solver: DASimpleFoam
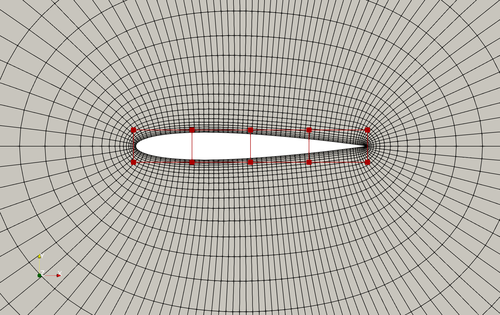
Fig. 1. Mesh and FFD points for the NACA0012 airfoil
To run this case, first download tutorials and untar/extract it. Since we use the pre-compiled DAFoam Docker image, we need to first start the Docker container (a light-weight virtual machine). If you use Linux, use the commands on this page. If you use MacOS, use the commands on this page. If you use Windows, use the commands on this page.
The above command will start a docker container, mount the current directory on your local OS (tutorials-master/NACA0012_Airfoil/incompressible) to the container’s mount directory, login to the container’s mount directory as dafoamuser, and set the relevant DAFoam environmental variables. You may see something like this on your terminal: dafoamuser@00fb6ceac4da:~/mount$.
Now you are on the DAFoam Docker container, run the preProcessing.sh script to generate the mesh:
./preProcessing.sh
Then, use the following command to run the optimization with 4 CPU cores:
mpirun -np 4 python runScript.py 2>&1 | tee logOpt.txt
The optimization progress will be printed to the screen and also written to logOpt.txt (we will elaborate on logOpt.txt later on this page). This case ran for 50 optimization iterations and took about 15 minutes with Intel 3.0 GHz CPU.
ctr+c or ctr+\. After the optimization is done, type exit to exit the docker container and free up the occupied memory../Allclean.sh to clean up the previous optimization results.Check this page for interpreting and post processing the optimization results.